How Cupping Therapy Works: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Cupping Therapy
Cupping therapy is an ancient form of alternative medicine that has been practiced for thousands of years. This therapeutic technique involves placing cups on the skin to create suction, which is believed to facilitate healing with blood flow, reduce pain, and promote relaxation. Originating from traditional Chinese and Middle Eastern cultures, cupping therapy has gained popularity worldwide as more people seek non-invasive treatment options.
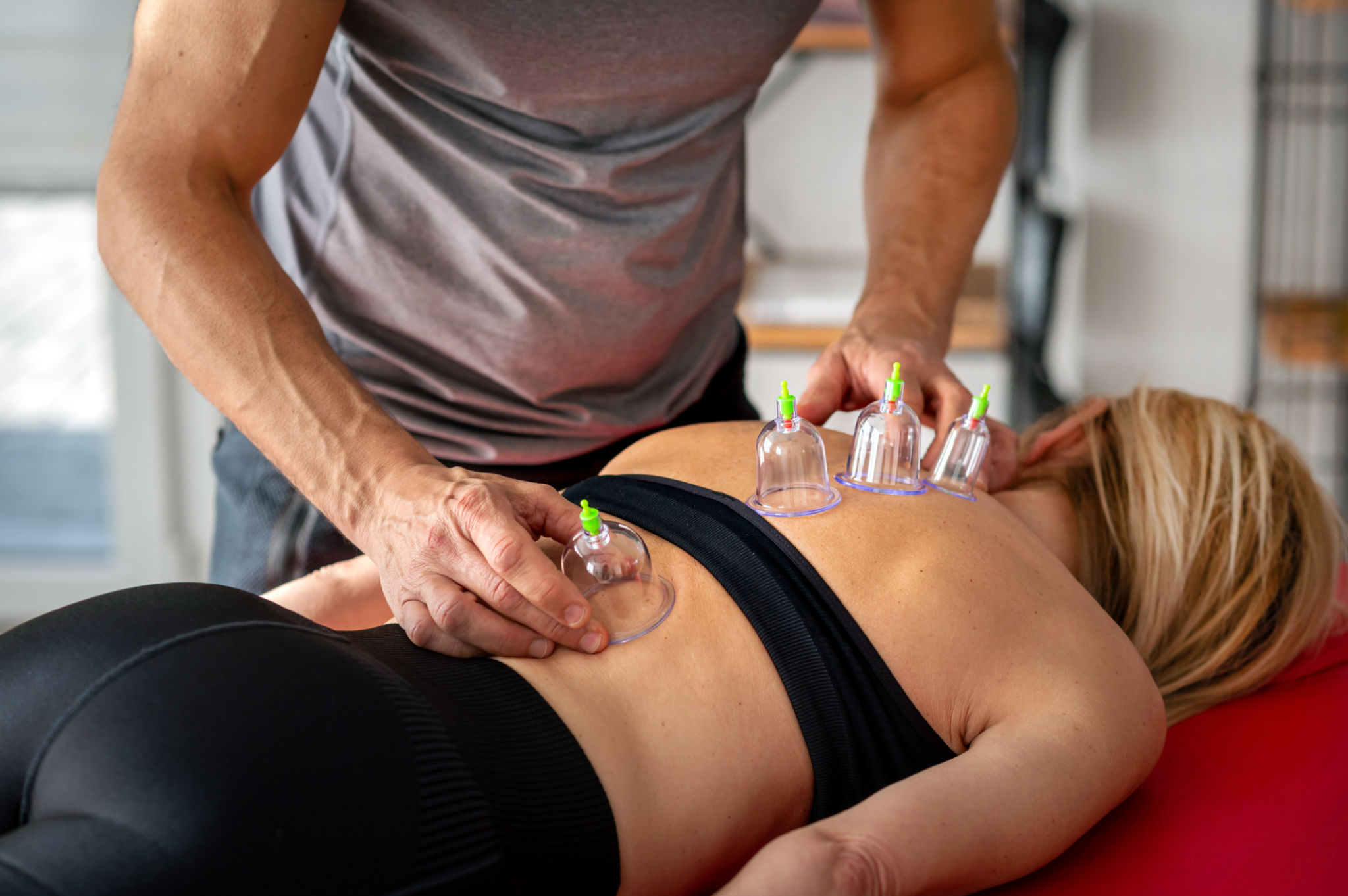
The Science Behind Cupping
But how exactly does cupping therapy work? The suction created by the cups draws the skin and superficial muscle layer into the cup. This process encourages blood flow to the affected area, which can help promote healing. The increased blood circulation might reduce muscle tension and improve overall circulation, leading to a sense of relief and rejuvenation.
Many practitioners believe that the suction helps facilitate the flow of "qi" in the body, a concept from traditional Chinese medicine that refers to life energy. By improving the qi flow, cupping is thought to help balance energy pathways and enhance overall well-being.
Types of Cupping Techniques
There are several types of cupping techniques that practitioners may use, each serving different purposes. Here are some common techniques:
- Dry cupping: This is the most common form, where cups are placed on the skin for a set period without any additional processes.
- Wet cupping: Also known as hijama, this technique involves making small incisions on the skin before applying the cups to draw out a small amount of blood.
- Fire cupping: Practitioners briefly introduce a flame into the cup before placing it on the skin, creating suction as the air cools.
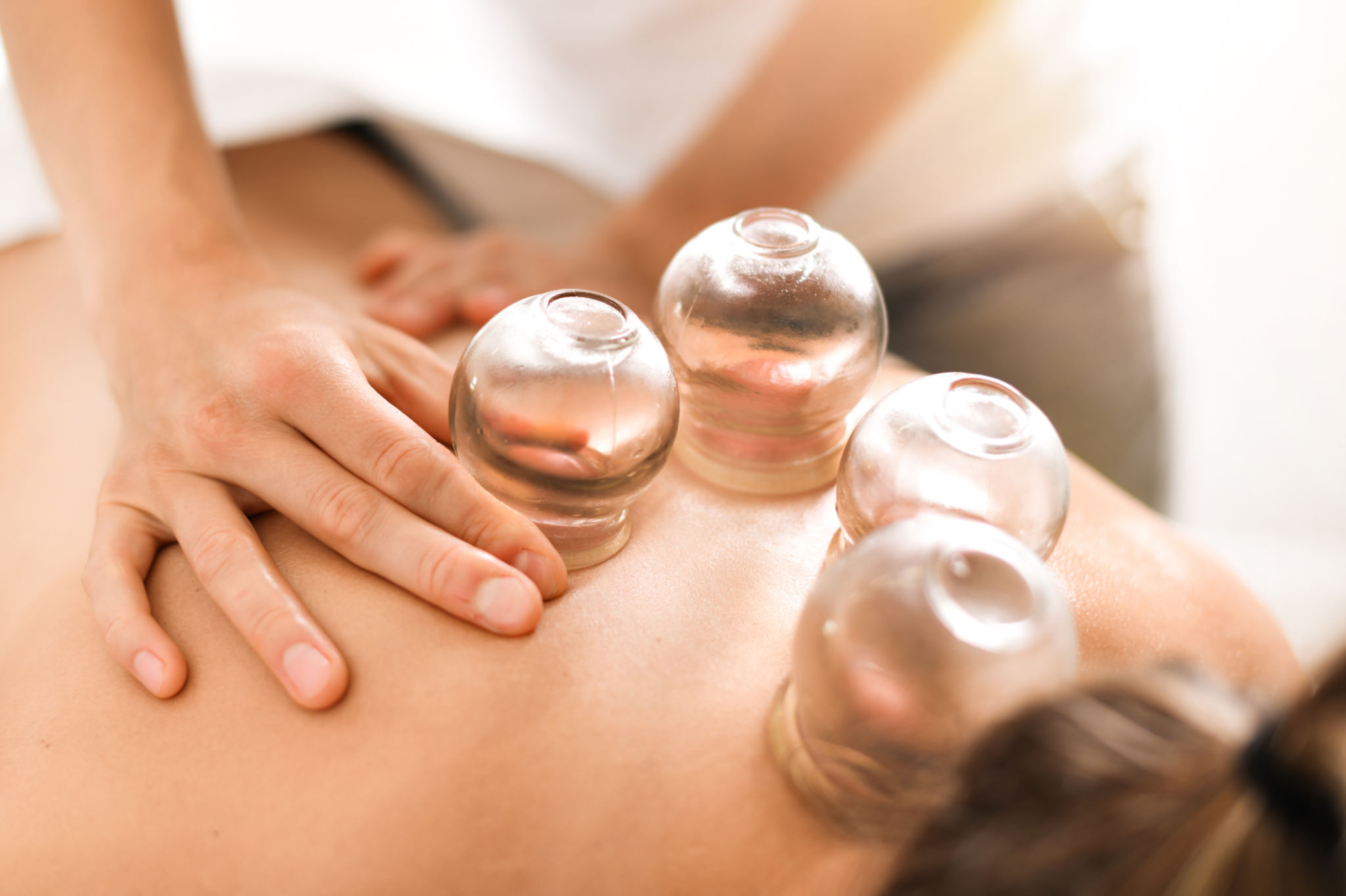

Benefits of Cupping Therapy
Cupping therapy offers a wide range of potential benefits that attract people seeking alternative healing methods. Some of the most frequently reported benefits include:
- Pain relief: Many individuals use cupping to alleviate chronic pain conditions such as back pain, neck pain, and migraines.
- Detoxification: By improving circulation, cupping may help remove toxins from the body through enhanced lymphatic drainage.
- Stress reduction: The relaxing sensation of cupping can promote mental well-being and reduce stress levels.
Cupping Therapy Session: What to Expect
If you're considering trying cupping therapy, it's essential to understand what a typical session involves. During a session, a practitioner will first evaluate your condition and discuss your medical history. They will then select the appropriate type and number of cups based on your specific needs.
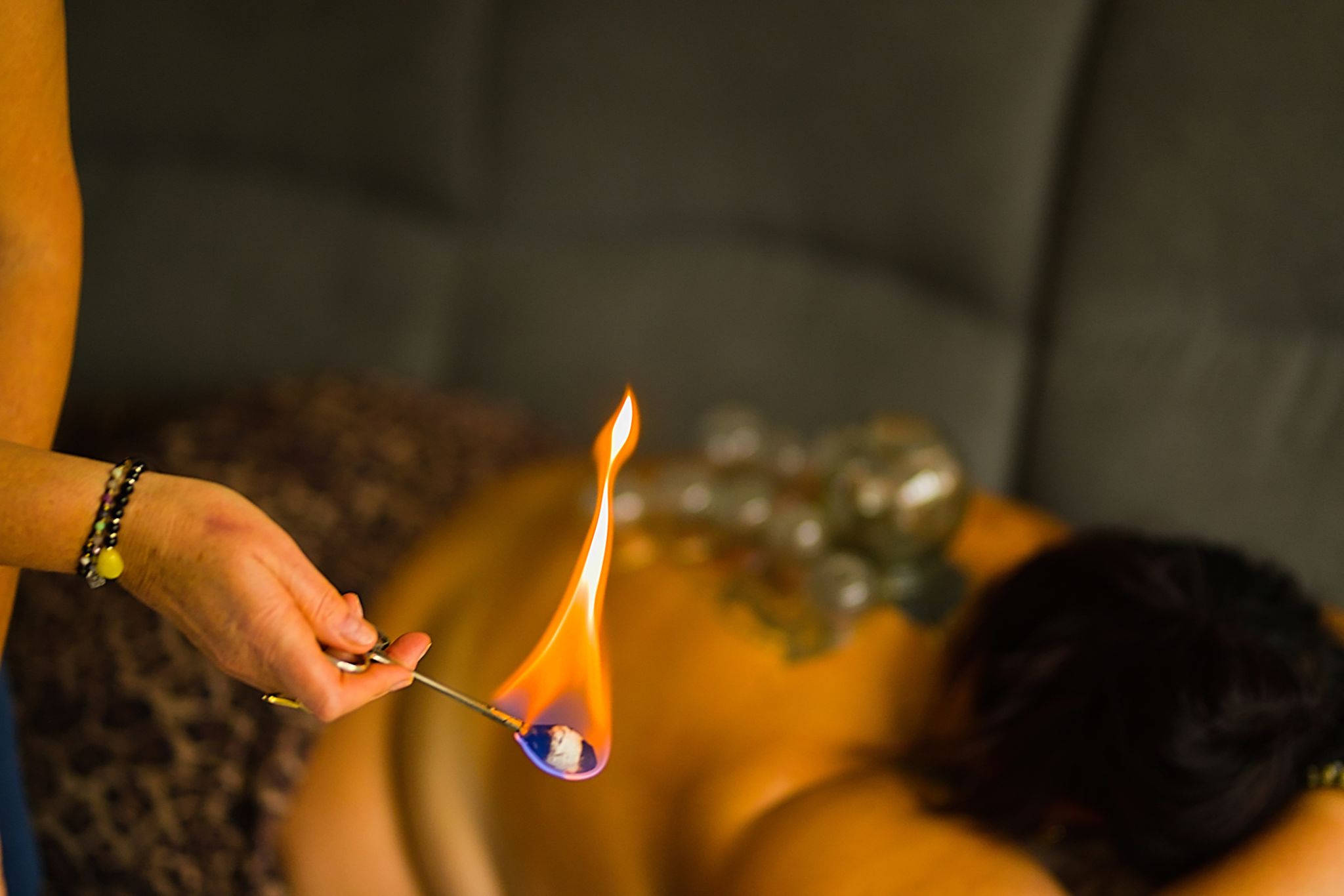

The practitioner will place the cups on your skin and leave them in place for a period of time, usually between 5 to 15 minutes. You may feel a slight tightening sensation as the cups create suction, but this should not be painful. Following the session, you might notice circular marks on your skin where the cups were placed. These marks are generally painless and fade within a few days.
Who Should Avoid Cupping?
While cupping therapy is generally considered safe for most individuals, there are some contraindications to be aware of. People with certain medical conditions should avoid this treatment or consult their healthcare provider before proceeding. These conditions include:
- Skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis in the treatment area
- Bleeding disorders or individuals on blood-thinning medications
- Pregnant women should avoid cupping over the abdomen or lower back
Finding a Qualified Practitioner
If you're interested in trying cupping therapy, it's crucial to find a qualified and experienced practitioner. Look for professionals who are certified in traditional Chinese medicine or have training in cupping techniques. Reading reviews and seeking recommendations can also help ensure you receive safe and effective treatment.
Cupping therapy can be a valuable addition to your wellness routine when performed correctly. As with any treatment, it's essential to approach it with an open mind and realistic expectations about its potential benefits.
